Positioning and Navigation
Introduction
Indoor navigation refers to the guidance of people inside buildings via an end device. Indoor navigation does not require automatic positioning, but in most cases it is part of the application.
Solutions for indoor and outdoor wayfinding can be provided in the form of HTML applications for mobile and desktop or stationary kiosk systems. A native app is not required for this.
Since GPS is unable to detect the floor of a building and the position resolution is very inaccurate due to shadowing, fixed Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) beacons are most commonly used as indoor positioning technology. The signal strengths of Wi-Fi access points can also be evaluated on Android devices. However, due to the higher latency for Wi-Fi scanning, the comparatively poor accuracy, and the exclusion of iOS devices, this is rarely used as a primary source for localization. A native app is required to determine the location based on BLE beacons.
Ultra-wideband (UWB) can also be used for indoor navigation and positioning. The battery-powered BLE/UWB locator beacons are convincing due to their low latency, and the position accuracy of less than 30 centimeters ensured by ultra-wideband with position queries up to 100 times per second.
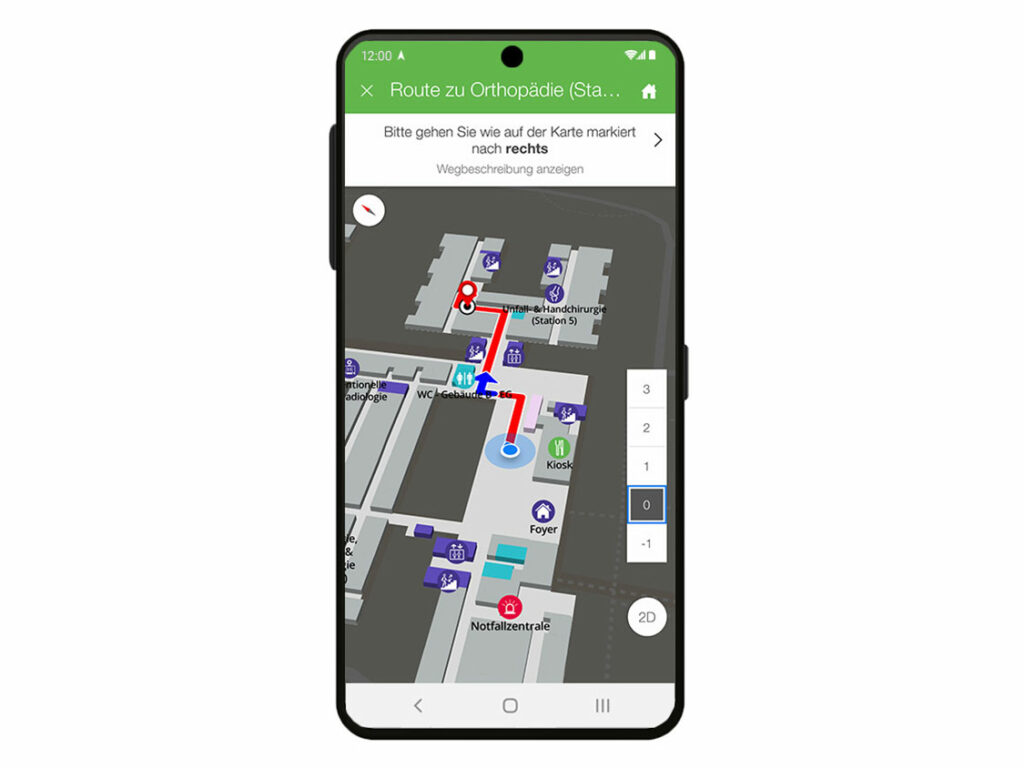
A typical feature of wayfinding is turn-by-turn instructions (information about route sequences on the map), which are automatically updated if automated positioning is activated.
Indoor navigation and positioning on the end device are one component in the system landscape offered by infsoft, which is, however, usually combined with other services to create higher added value for the user. This is illustrated by the example of the Workplace Experience solution.
Positioning Technologies
Automatic positioning on mobile devices is usually implemented as a client-based application. This means that the position is determined directly on the smartphone and is not acquired via a server. Since the position data does not leave the device, this is explicitly advantageous with regard to data protection considerations. An app is required to determine the location, otherwise the necessary system information (Bluetooth/UWB) cannot be accessed.
A server-based approach is also possible, but is associated with technical challenges and significantly higher latency times. Read more about the differences between client-based and server-based positioning here.
The most common positioning technologies for positioning and navigation are Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), Wi-Fi and Ultra-Wideband. For positioning with a combination of both Ultra-Wideband and Bluetooth Low Energy technologies, we rely on infsoft Locator Beacons.
Positioning technologies
Hardware
In order to increase the positioning accuracy, the smartphone sensors – for example, magnetic field, compass, air pressure, barometer, acceleration sensors, and gyroscope – are always addressed, regardless of the positioning technology used.
Deployed Software
The infsoft setup tools can be used to set up positioning and indoor navigation.
Implementation in infsoft Products
Positioning and indoor navigation is implemented as part of infsoft Wayfinding and infsoft Workplace Experience.
infsoft Wayfinding
infsoft Wayfinding facilitates orientation in buildings and on campus areas. In addition to relevant points of interest, the user’s own location can be viewed on a digital map. Using turn-by-turn navigation, the user is guided to their destination.
infsoft Workplace Experience
In addition to providing wayfinding, infsoft Workplace Experience offers further relevant functions. These include, for example, planning the journey to the office, booking meeting rooms, viewing the occupancy of desks, networking with colleagues and much more.