RFID is one of the most versatile technologies in the field of indoor localization and can be used in nearly every industry. But how does an RFID system work and what advantages does it offer?
HOW DOES RFID WORK?
RFID stands for “Radio-Frequency Identification” and describes systems that use radio waves to identify objects or persons. In a passive RFID system, there is a transponder (“RFID tag”) on whose microchip data (usually a serial number) are stored, which can be forwarded wirelessly to a reader. The reading unit, e.g., an infsoft Locator Node, generates an energy field that activates the RFID tag. In order to enable information exchange, the distance between Locator Node and transponder must be less than one meter (remote-coupling).
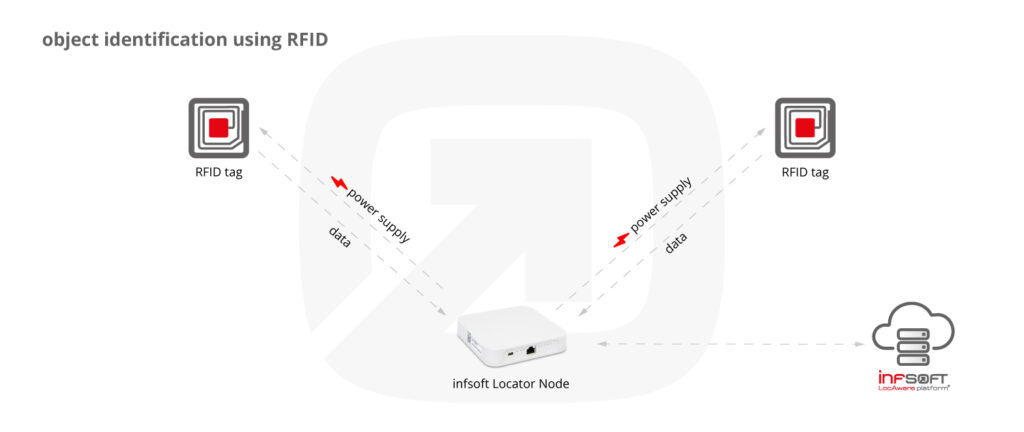
WHAT CAN RFID BE USED FOR?
No matter which industry you are thinking of – since it is a very versatile technology, RFID can be used almost everywhere. Common applications are systems for access control, time recording or inventory control in logistics. Since reliable identification of products or objects is required in many industries, RFID is particularly suitable as an asset tracking solution.
WHAT ARE THE ADVANTAGES OF THIS TECHNOLOGY?
Since passive transponders do not have their own energy source, they are almost maintenance-free. As a result, initial acquisition costs will pay off in the long term in most cases. RFID tags do not require visual contact with the reader, and they are durable against impact and environmental factors.
COMBINATION WITH OTHER POSITIONING TECHNOLOGIES
Combining RFID systems with other positioning technologies can solve the biggest problem of RFID technology: objects equipped with RFID tags can only be located at a specific point – namely exactly where RFID hardware (e.g., Locator Nodes) has been installed. However, if for example a forklift truck is equipped with an infsoft Locator Node, whose sensors not only respond to RFID, but also to Ultra-wideband (UWB), a link between the position data of the forklift truck and the identification times of RFID-tagged goods can be established. As a result, the efficiency of logistics processes can be significantly improved, since in addition to spot detection, real-time material flow control is also made possible.
More information on all things RFID and exciting use cases here.
Find answers to the most important questions regarding indoor localization with UWB here: info portal ultrawideband.io