Client-based/server-based positioning: What are the differences and which method is suitable for which application scenario?
CLIENT-BASED INDOOR POSITIONING
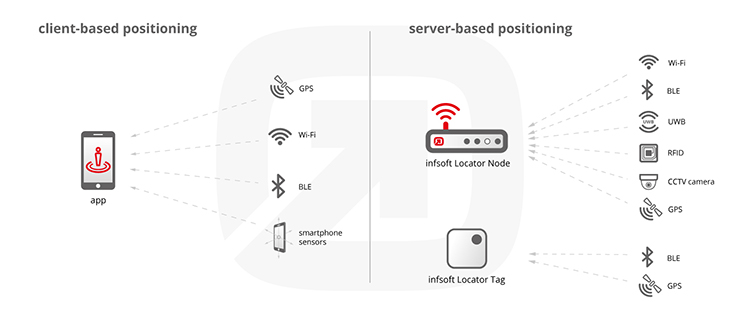
When using client-based positioning, positioning is done directly on the device. There must be an adequate app installed which analyzes the signals of Wi-Fi access points, LED and/or beacons. The app contains a database with which the signal strength is matched. This way, the device can detect its position via fingerprinting without being connected to an access point. The location owner can send the visitor messages – for example location based ads and useful information. Client-based positioning means that the user’s data don’t leave the phone as long as it’s only about positioning.
Client-based positioning is mainly suitable for indoor navigation in retail, at trade fairs, airports, railway stations and in museums and hospitals. It is of big advantage that existing Wi-Fi access points can be used. Projects focusing exclusively on Wi-Fi will exclude all Apple devices because they cannot determine their position via Wi-Fi.
SERVER-BASED INDOOR POSITIONING
Server-based positioning means that a Wi-Fi enabled device, a tag or a Bluetooth beacon sends out a unique key (MAC address, UUID). Specific hardware captures the signals and transmits them to a server which calculates the position via finger printing based on signal strengths and coordinates.
Server-based positioning detects all devices, an app is not required. This method is especially suitable for asset and personnel tracking. For example, it is possible to detect the position of medical instruments at a clinic, vehicles in industrial facilities and goods in retail. Geofencing enables automatic notifications when object leave a defined area (theft protection). Location owners can profit from information about visitor flows. Employers can detect the current position of their employees, for example at a large exhibition stand. In most cases, tracking is done anonymously.
If you have any questions concerning indoor positioning techniques, don’t hesitate to contact us.